DOI number:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2023.01.043
Journal:Journal of the European Ceramic Society
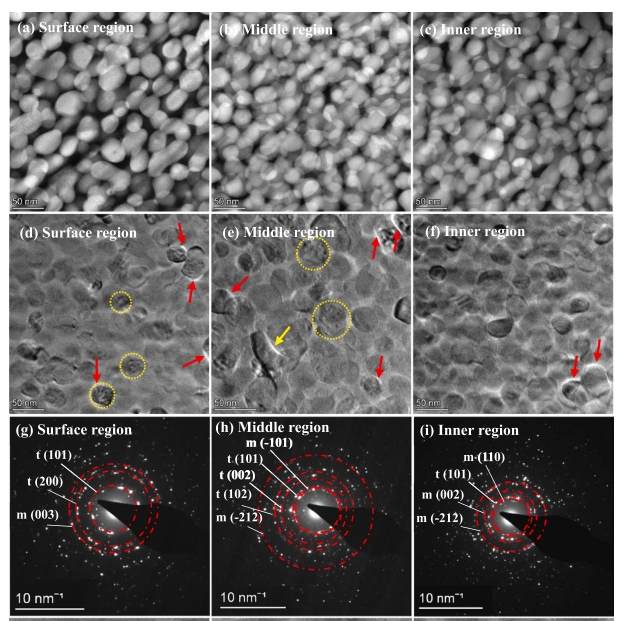
Abstract:Developing new radiation-resistant materials and understanding the structural damages caused by radiation are persistent goals of material scientists. Here, we report on the structural integrity and damage to ZrO2-SiO2 nanocrystalline glass-ceramics after radiation with 1.4 MeV He ions at three different fluences: 1.0 × 1016 ions/cm2 (low), 5.0 × 1016 ions/cm2 (moderate), and 1.0 × 1017 ions/cm2 (high) at 500ºC. Grazing incident X-ray diffraction shows the tetragonal-ZrO2 to monoclinic-ZrO2 phase transformation induced by microstrain from the irradiation. The addition of yttrium indicated tetragonal-ZrO2 stabilization effect during irradiation. The irradiated glass-ceramics show a Raman signal-enhancement effect probably related to the electronic structure changes of the amorphous SiO2 component in the glass-ceramics. The formation of microcracks and lattice defects within ZrO2 nanocrystallites is the main structural damage caused by irradiation. There was no observable amorphization of ZrO2 nanocrystallites due to irradiation. No obvious He bubbles were detected, either. The formation of microcracks results in a decrease of in the nanohardness of the glass-ceramics. The results provide fundamental experimental data to understand the structural integrity and damage caused by radiation, which could be useful to design radiation‐resistant nanocrystalline glass-ceramics for extremely radioactive environments.
Co-author:Bohan Wang, Yabin Zhu*, Tielong Shen, Ying Deng, Guofu Xu, Jiwu Huang, Yucheng Feng, Liangting Sun, Wei Xia
First Author:Le Fu*
Volume:43
Page Number:2624-2633
Translation or Not:no
Links to published journals:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0955221923000560