DOI number:10.1016/j.matchar.2025.115334
Journal:Materials Characterization
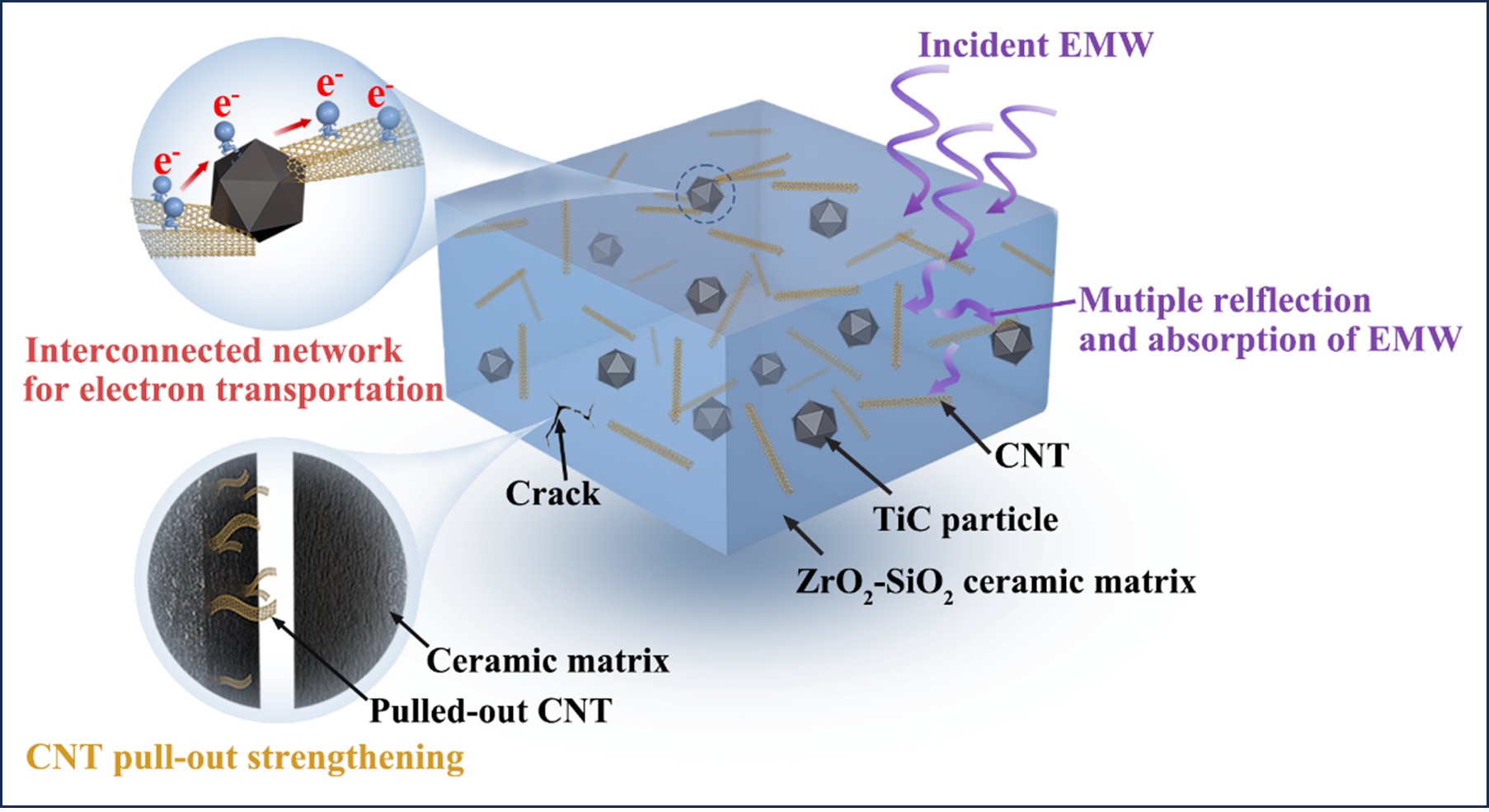
Abstract:In this study, we sought to develop structure-function integrated ZrO2-SiO2 ceramic nanocomposites by simultaneously incorporating one-dimensional (1D) carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and three-dimensional (3D) Ti3AlC2 MAX phase. The CNTs and Ti3AlC2 were introduced into the ZrO2-SiO2 precursor powder via a straightforward wet ball milling process. CNTs maintained excellent structural stability during sintering, whereas the Ti3AlC2 decomposed into Al and TiC. The flexural strength of the nanocomposite was enhanced by 34 % attributed to the pull-out strengthening effect of the CNTs. The uniformly distributed 1D CNTs and the in-situ formed 3D TiC particles created an interconnected network within the ceramic matrix, thereby providing efficient pathways for electron transport. Consequently, the electrical conductivity and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of the nanocomposites were markedly improved. This study demonstrates an effective approach to developing structure-function integrated ceramic composites by exploiting the dimensional differences and synergistic interactions between the filler phases.
Co-author:Zihua Lei, Wenqian Pan, Yang Li, Songlin Ran
First Author:Wenjun Yu
Correspondence Author:Le Fu*
Volume:25
Translation or Not:no
Links to published journals:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1044580325006230