Inhibiting coarsening of yttrium-stabilized zirconia nanograins via dopant segregation at grain boundaries
发布时间:2025-11-22
点击次数:
DOI码:10.1016/j.matchar.2025.115803
发表刊物:Materials Characterization
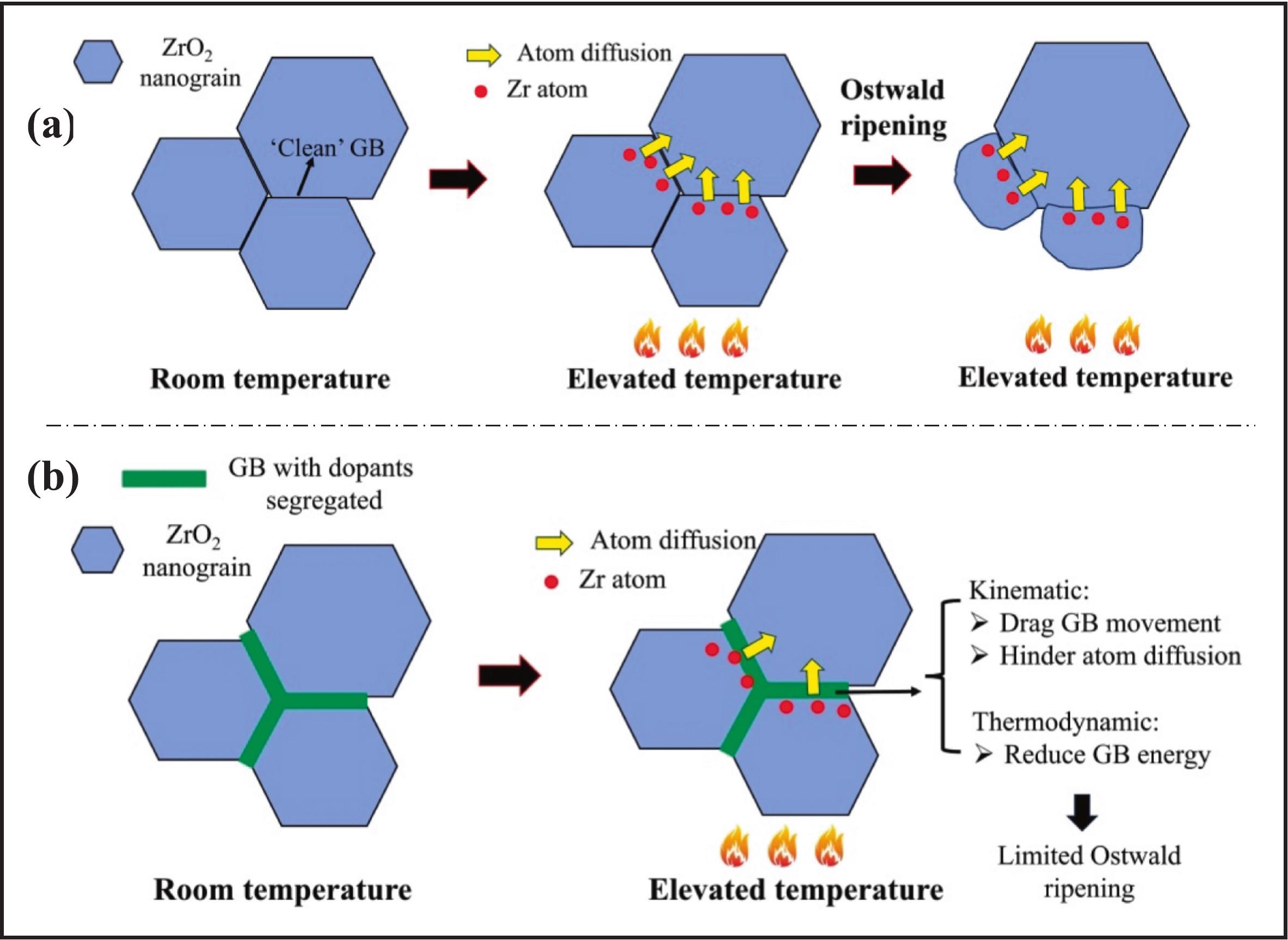
摘要:In this study, we aimed to suppress thermally-induced coarsening of 3 mol% yttrium-stabilized zirconia (3YSZ) nanograins through dopant segregation at grain boundaries (GBs). For this purpose, three dopants—Si, La, and Ca—were selected based on their potentially strong segregation tendencies. Three doping strategies were investigated: single-element doping (La), binary-element doping (Si and La), and ternary-element doping (Si, La, and Ca). The results indicated that a portion of the dopants dissolved within the ZrO2 grains as solute atoms, whereas the remainder segregated at GBs or accumulated at triple junctions in the form of a glassy phase. Although the ZrO2 grain sizes measured from SEM images were larger than those calculated using the Scherrer equation based on XRD results, the coarsening trends obtained from both methods were largely consistent. All three doping strategies demonstrated a coarsening inhibition effect during post-sintering thermal treatment up to 1250 °C, with the binary-element doping exhibiting the most pronounced inhibitory effect. This inhibition of coarsening can be attributed to the dual effects of doping: it not only kinematically restricts the diffusion of Zr and O atoms across GBs and exerts a drag force on GB movement, but also thermodynamically reduces the GB energy.
合写作者:Wenjun Yu, Zihua Lei, Mingxi Deng
第一作者:Le Fu*
通讯作者:Yang Liu*
卷号:230
页面范围:115803
是否译文:否
发表时间:2025-11-21
发布期刊链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1044580325010927