2025-09-09:祝贺21级博士生周金伟和24级直博生梁韦泓研究论文在ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces发表!
发布时间:2025-09-09
点击次数:
Binder-Drive Interfacial Solvation Modulation Enables LiF-Rich SEI for Durable Silicon-Carbon Anodes
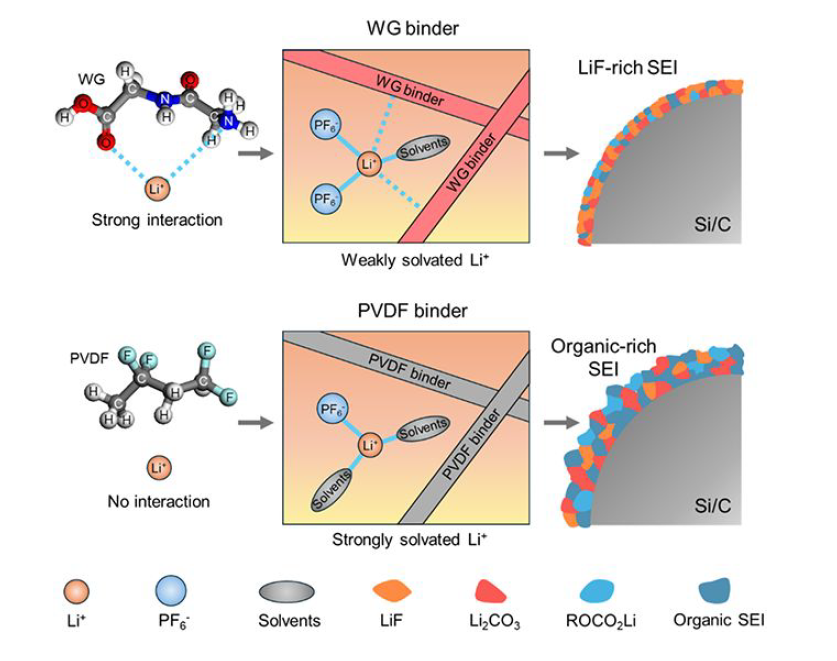
Silicon–carbon (Si/C) anodes have emerged as promising alternatives to conventional graphite anodes for high-energy lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), owing to their higher specific capacity than graphite and enhanced cycling stability over pure silicon. However, the unstable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) due to large volume changes during cycling is still a key bottleneck limiting their electrochemical performance. To address this critical limitation, the present study introduces wheat gluten (WG), a biomass-derived material from wheat, as a low-cost and sustainable binder for Si/C anodes. WG, rich in organic functional groups such as −COOH and −NH2, exhibits unique coordination capabilities with Li+. When employed as a binder, WG effectively induces the formation of Li+ solvated structures that weaken solvent coordination at the electrode surface/interface. This behavior facilitates the preferential growth of a LiF-rich SEI, thereby enhancing interfacial stability and mitigating capacity fade. Consequently, Si/C anodes employing WG binder (Si/C-WG) demonstrate remarkable cycling performance,delivering 95.9% capacity retention after 300 cycles at 0.5 A g–1, far surpassing that of conventional poly(vinylidene difluoride) (PVDF) binder, which retains only 59.5%. This study presents a novel strategy for designing functional binders optimized for Si/C anodes, offering critical insights to advance the development of high-performance anode materials in LIBs.