Coastal Subsidence Monitoring Associated with Land Reclamation Using the Point Target Based SBAS-InSAR Method: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China
发布时间:2018-04-25
点击次数:
影响因子:4.848
DOI码:10.3390/rs8080652
发表刊物:Remote Sensing
关键字:Coastal subsidence; Land Reclamation; PT-based SBAS-InSAR; Sea Level Rise; Shenzhen
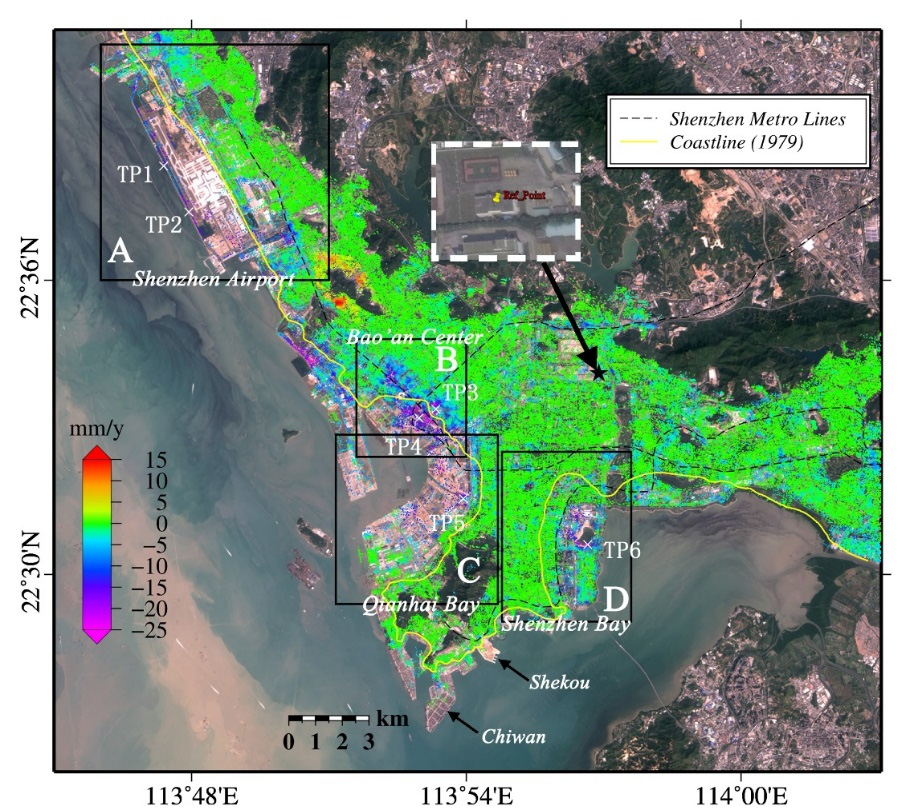
摘要:Shenzhen, the first special economic zone of China, has witnessed earth-shaking changes since the late 1980s. In the past 35 years, about 80 km(2) of land has been reclaimed from the sea in Shenzhen. In order to investigate coastal vertical land motions associated with land reclamation, we proposed an elaborated Point Target (PT) based Small Baseline Subset InSAR (SBAS-InSAR) strategy to process an ENVISAT ASAR ascending and descending orbits dataset both acquired from 2007 to 2010. This new strategy can not only select high density PTs but also generate a reliable InSAR measurement with full spatial resolution. The inter-comparison between InSAR-derived deformation velocities from different orbits shows a good self-consistency of the results extracted by the elaborated PT-based SBAS-InSAR strategy. The InSAR measurements show that the reclaimed land is undergoing remarkable coastal subsidence (up to 25 mm/year), especially at the Shenzhen Airport, Bao'an Center, Qianhai Bay and Shenzhen Bay. By analyzing the results together with land reclamation evolution, we conclude that the ground deformation is expected to continue in the near future, which will amplify the regional sea level rise.
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:652
学科门类:工学
一级学科:测绘科学与技术
文献类型:J
卷号:8
期号:8
是否译文:否
发表时间:2016-08-13
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/8/8/652
附件:
上一条: Continent-Wide 2-D Co-Seismic Deformation of the 2015 Mw 8.3 Illapel, Chile Earthquake Derived from Sentinel-1A Data: Correction of Azimuth Co-Registration Error
下一条: Deriving Spatio-Temporal Development of Ground Subsidence Due to Subway Construction and Operation in Delta Regions with PS-InSAR Data: A Case Study in Guangzhou, China