SAR Interferometric Baseline Refinement Based on Flat-Earth Phase without a Ground Control Point
发布时间:2022-02-17
点击次数:
影响因子:4.848
DOI码:10.3390/rs12020233
发表刊物:Remote Sensing
关键字:Synthetic aperture radar interferometry; InSAR baseline estimation; flat-earth phase; baseline refinement.
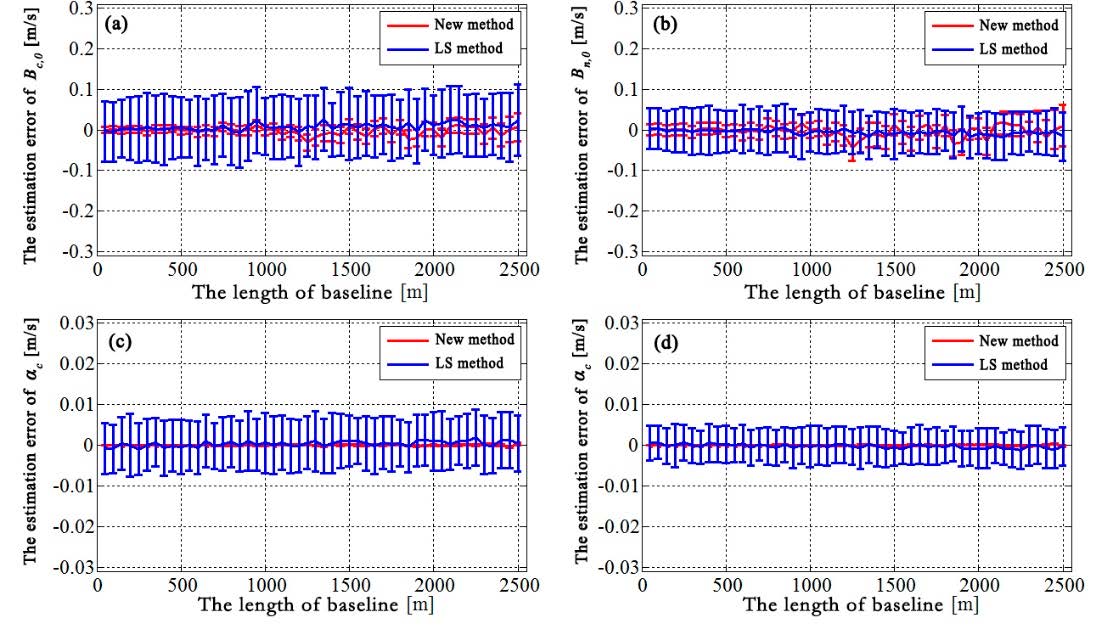
摘要:Interferometric baseline estimation is a key procedure of interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data processing. The error of the interferometric baseline affects not only the removal of the flat-earth phase, but also the transformation coefficient between the topographic phase and elevation, which will affect the topographic phase removal for differential interferometric SAR (D-InSAR) and the accuracy of the final generated digital elevation model (DEM) product for interferometric synthetic aperture (InSAR). To obtain a highly accurate interferometric baseline, this paper firstly investigates the geometry of InSAR imaging and establishes a rigorous relationship between the interferometric baseline and the flat-earth phase. Then, a baseline refinement method without a ground control point (GCP) is proposed, where a relevant theoretical model and resolving method are developed. Synthetic and real SAR datasets are used in the experiments, and a comparison with the conventional least-square (LS) baseline refinement method is made. The results demonstrate that the proposed method exhibits an obvious improvement over the conventional LS method, with percentages of up to 51.5% in the cross-track direction. Therefore, the proposed method is effective and advantageous.
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:233
学科门类:工学
一级学科:测绘科学与技术
文献类型:J
卷号:12
期号:2
页面范围:233
是否译文:否
发表时间:2020-01-09
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/12/2/233
附件: