Designing activated carbon and porous carbon nanofibers for insight into their differences in adsorption affinity mechanisms of VOCs
发布时间:2024-09-30
点击次数:
DOI码:10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.159961
所属单位:中南大学
发表刊物:Applied Surface Science
关键字:Activated carbon nanofibers; Adsorption; Density functional theory; Porous carbon; Volatile organic compounds
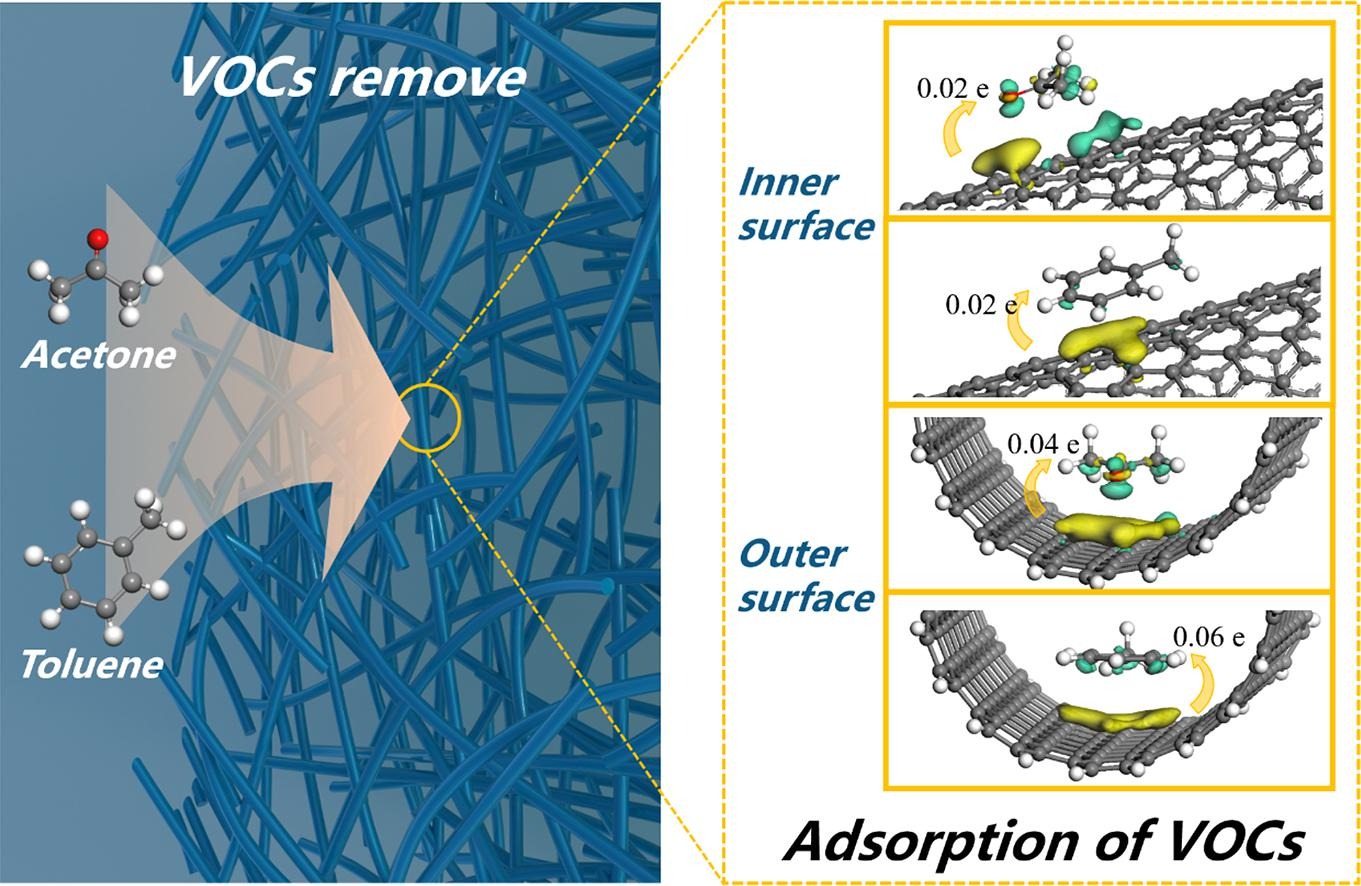
摘要:The adsorption technology has been considered as an effective and economical strategy to control volatile organic compounds (VOCs) through various types of porous materials. As two potential porous materials, activated carbon and carbon nanofibers were synthesized as VOCs adsorbents. In order to investigate the difference in the adsorption of VOCs between activated carbon and carbon nanofibers, the specific surface area, pore structure and chemical functional groups of VOCs adsorbent were analyzed. In particular, the carbon nanofibers (CNF) activated at 800 ℃ showed an excellent specific surface area (2524 m2·g−1), abundant pores (1.66 mL·g−1), and rich functional groups (N: 8.29 at%). Meanwhile, the carbon nanofibers had a better adsorption performance for acetone (1069.82 mg·g−1) and toluene (427.72 mg·g−1) than activated carbon materials. Furthermore, the theoretical calculations were conducted to reveal the mechanism of favorable adsorption on the CNFs. The theoretical adsorption energies of CNF are −31.9 kJ·mol−1 (acetone) and −67.5 kJ·mol−1 (toluene), respectively, which have more favorable adsorption sites and stronger charge redistribution than activated carbon. This research guided the approach to obtain the porous carbon nanofibers and provided the evidence for CNFs (curved carbon) exhibiting a better adsorption ability to VOCs.
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:159961
卷号:659
ISSN号:01694332
是否译文:否
发表时间:2024-06-30
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169433224006743?via%3Dihub