点击次数:
DOI码:10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c06929
所属单位:中南大学
发表刊物:Journal of Physical Chemistry C
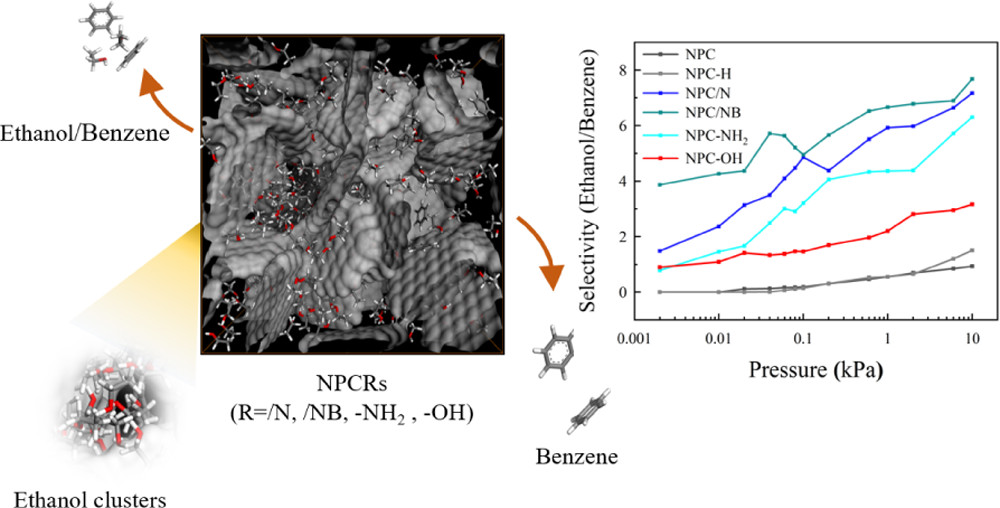
摘要:Grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations combined with molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and density functional theory calculations are used to study the adsorption and separation potentials of surface-functionalized nanoporous carbons (NPCR, R = /N, /NB, -NH2, and -OH) for ethanol and benzene at 293 K. The surface-functionalized NPCs present a higher ethanol uptake (maximum = 5.61 mmol/g at 0.002 kPa) at a lower pressure range for their remarkable electrostatic affinity and strong electrostatic interaction (hydrogen bonding interaction) with ethanol. The MD simulation shows that surface modification enhances the ethanol molecular clustering effect under a pore occupancy less than 0.6, which further improves the ethanol adsorption performance. There is, however, no direct evidence that surface functionalization can enhance the benzene uptake by NPCs. Specifically, among the surface-functionalized NPCs, NPC/NB exhibits the highest ethanol/benzene selectivity under the entire pressure range (∼3.8 at 0.002 kPa and ∼8.6 at 10 kPa). Furthermore, NPC/NB and NPC/N have a better ethanol/benzene separation performance than NPC-NH2 and NPC-OH. Electrostatic potential analysis shows that heteroatom doping impels the ethanol molecule cluster on surface graphite layers, which inhibits the benzene adsorption capacity of NPC/N and NPC/NB in the process of mixture adsorption. This study provides a possible strategy in the preparation of NPC for the ethanol/benzene mixture adsorptive separation.
论文类型:期刊论文
卷号:125
期号:42
页面范围:23463 - 23473
ISSN号:19327447
是否译文:否
收录刊物:SCI