Impact Factor:5.349
DOI number:10.3390/rs15071765
Journal:Remote Sensing
Key Words:GBSAR; atmospheric delay; displacement estimation; spatial and temporal features; bridge vibration monitoring
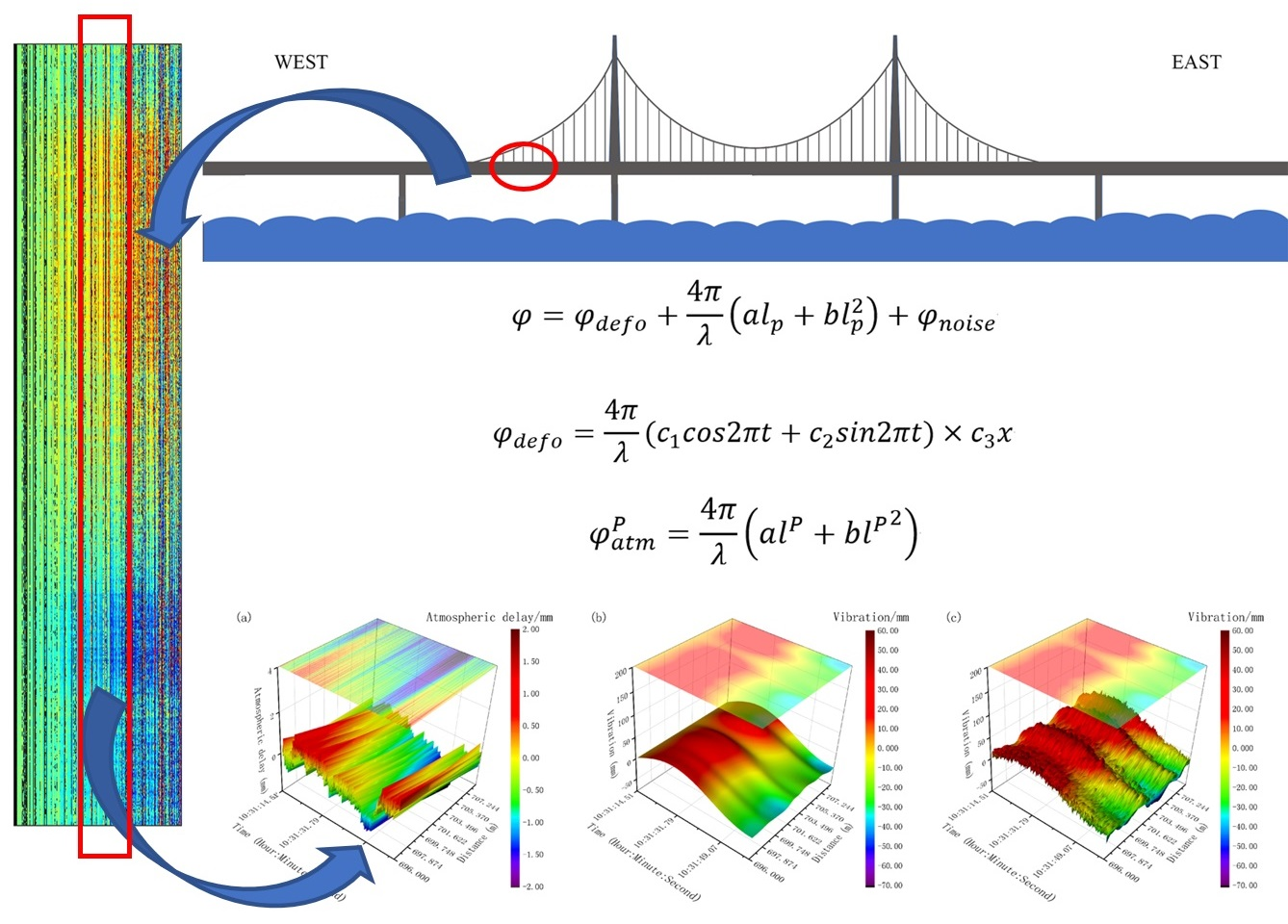
Abstract:Atmospheric delay is the primary error in ground-based synthetic aperture radar (GBSAR). The existing compensation methods include the external meteorological data correction method, the polynomial fitting method, and the persistent scatterers SAR interferometry (PSInSAR) calibration method. Combining the polynomial fitting and the persistent scatterers targets is the most popular method of GBSAR atmospheric delay compensation. However, the displacement component of the coherent target is always ignored in the atmospheric delay compensation, which is unpractical. A joint estimation method of ground displacement and atmospheric model parameters is developed in this paper. The displacement component is determined by the spatial and temporal features of the objects. The atmospheric delay component is regarded as a systematic error represented by a quadratic polynomial related to distance. The result is resolved by the least-square method. Compared to the existing method, the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of the proposed method had a significant improvement in the validation experiment. In the real in situ experiment, the time series obtained by the GBSAR had a similar trend to that acquired by the Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver. It is indicated that the proposed method can lead to a better deformation estimation by taking the deformation component into account in the atmospheric compensation.
Indexed by:Journal paper
Discipline:Engineering
First-Level Discipline:Surveying and Mapping
Document Type:J
Translation or Not:no
Included Journals:SCI
Links to published journals:https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071765