DOI number:10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3333960
Journal:IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing
Key Words:PS-InSAR,Zero-temporal baseline combination,Time-domain phase difference,Phase unwrapping,Deformation time series
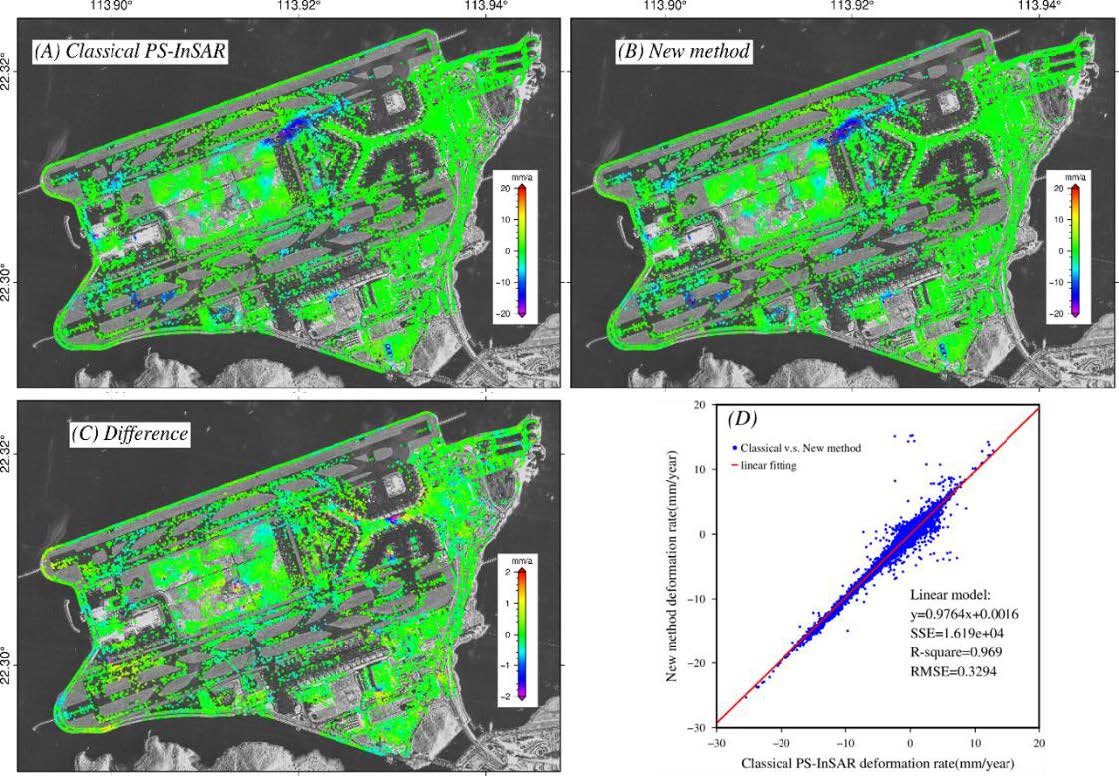
Abstract:To separate and unwrap the residual topographical and deformation components from the wrapped phases are the kay issues for Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PS-InSAR) technique. The currently methods, such as grid-search method based on the assumption that the deformation in time-domain is linear, or the LAMBDA method that needs priori information to construct the pseudo-observations, etc., are still difficult to trade off accuracy against efficiency. In this paper, we propose a new method to separate and unwrap the differential phases for PS-InSAR by dividing them into residual topographical phase and differential deformation phases and performing the phase unwrapping separately. Firstly, we calculate phase ambiguities caused by residual topographical error by zero-temporal baseline combination and single parameter grid-search method. The calculated residual topographical error is used to separate the differential phases dominated by deformations from the original differential phases of PS-InSAR. Then we proposed time-domain differentiation to unwrap differential phases dominated by deformations without any assumption of deformation model in time-domain. The performance of the proposed method is tested by both simulated and real datasets. The experimental results show that, compared with classic PS-InSAR, the accuracy of residual topographical error estimation is comparable, however there is an accuracy improvement of 34.4% for the deformation parameter estimation and 35.7% for nonlinear deformation time series extraction, as well as an improvement of 20∼40 times in computational efficiency.
Indexed by:Journal paper
Discipline:Engineering
First-Level Discipline:Surveying and Mapping
Document Type:J
Translation or Not:no
Included Journals:SCI