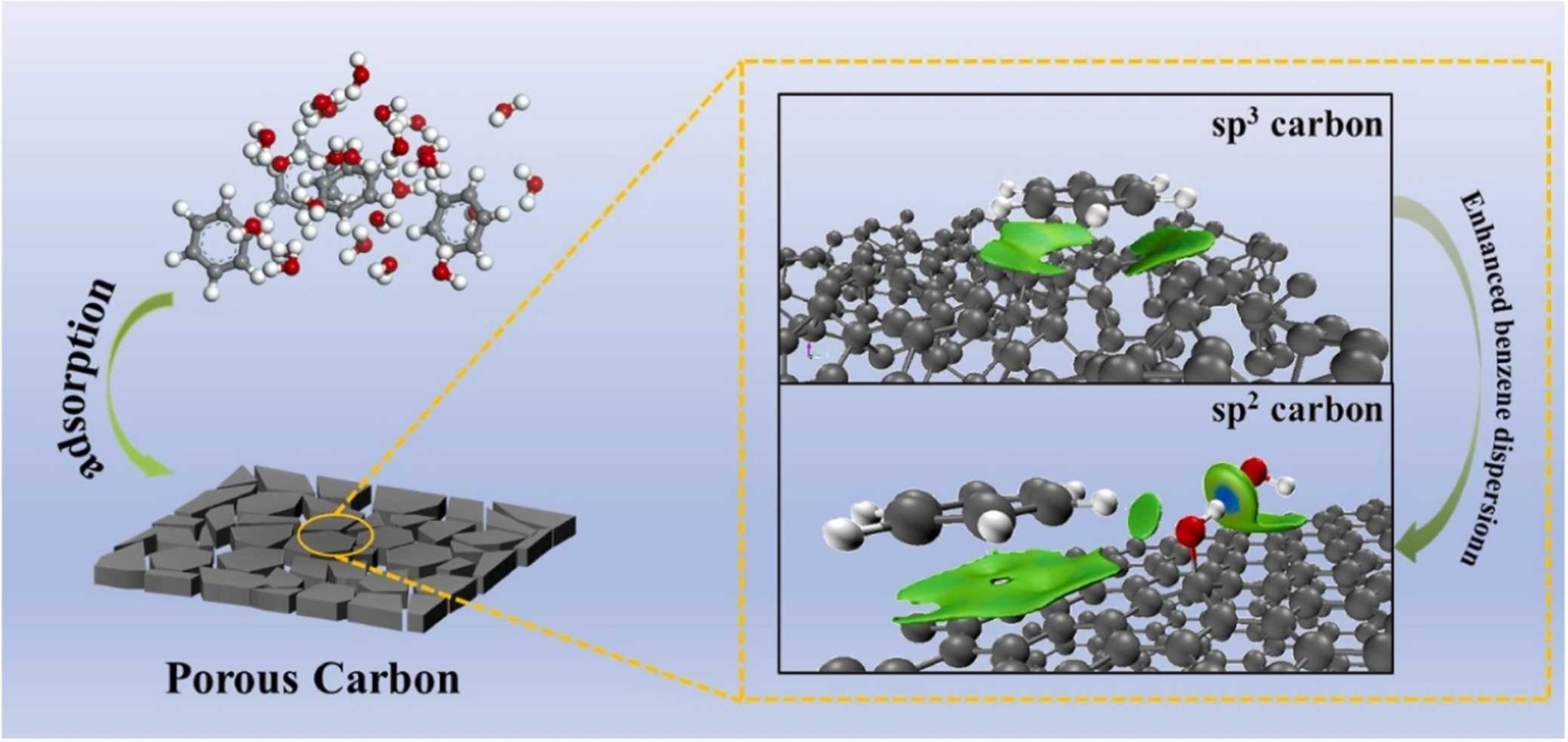
Mechanistic effects of graphitization and oxygen functional groups on benzene competitive adsorption of porous carbon under high humidity conditions
发布时间:2024-09-29
点击次数:
DOI码:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2024.135383
所属单位:中南大学
发表刊物:Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects
关键字:VOCs adsorptionPorous carbonGraphitizationOxygen functional groupGCMC&DFT
摘要:Porous carbon is an ideal adsorbent for the elimination of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) attributed to their price, availability and excellent adsorption capacity. However, there are significant variation in the adsorption capacity and adsorption selectivity of different precursors for VOCs under humid conditions after modification because of the differences in their own structural properties. In this study, graphitized hydrophobic porous carbon with excellent specific surface area was successfully synthesized by selecting bamboo fiber, maize, coconut husk and coal as precursors and potassium hydroxide as an activator. Among them, the dynamic adsorption capacity of benzene in the sample with bamboo fiber as precursor was maintained at 74.7 % under the high humidity condition (RH90 %) compared with the dry state (RH0 %). Grand Canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations and weak interaction force analyses showed that enhanced dispersion attraction between graphitized carbon surfaces and benzene molecules in comparison to disordered carbon surfaces. The existence of oxygen functional groups enhanced the interaction between porous carbon and water through hydrogen bonding leading to preferential adsorption of water molecules, which resulting in the decrease of their adsorption performance in wet condition. This research provided theoretical and experimental views of the effects of graphitization and oxygen functional groups on the competitive adsorption capture of benzene and water by porous carbon, which further provided a reliable approach to synthesizing porous carbon with high adsorption capture for benzene removal in high humidity environments.
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:135383
卷号:703
是否译文:否
发表时间:2024-09-29
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927775724022477?via%3Dihub