Nanoflower-like δ-MnO2 exhibits excellent ozone decomposition under harsh conditions: The influence of potassium ion
发布时间:2024-09-29
点击次数:
DOI码:10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160769
所属单位:中南大学
发表刊物:Applied Surface Science
关键字:Manganese dioxide; Oxygen vacancy; Ozone removal; Potassium ion; Water resistance
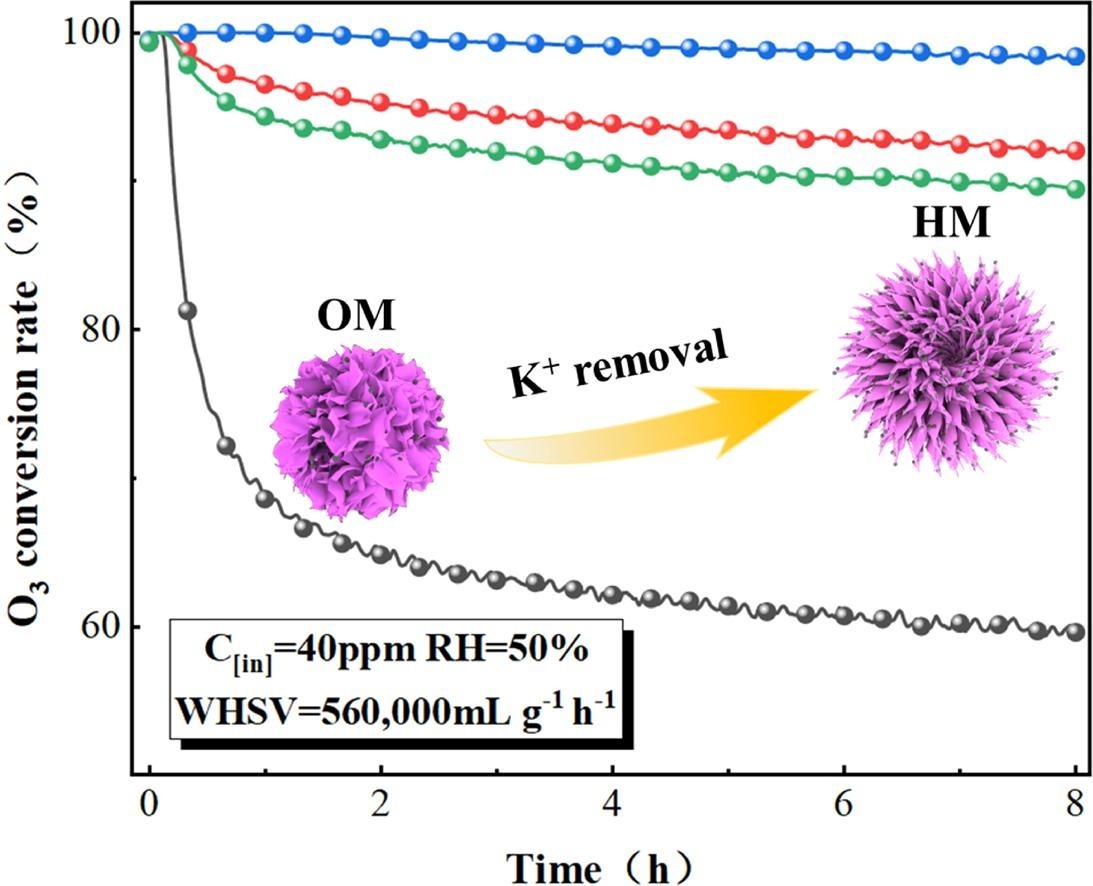
摘要:Near ground level and in indoor environments, ozone is extremely hazardous, and its removal under harsh conditions (high humidity and high air speed) poses a significant challenge. In this work, a series of catalysts for ozone decomposition were prepared by simple redox reactions and acid treatment under normal pressure and room temperature. The sample H20M-3 (1:20 solid–liquid mass ratio and 3 h stirring time) exhibited excellent ozone decomposition and water resistance properties. Ozone conversion efficiency exceeded 99 % in 8 h at 40 ppm ozone, a temperature of 30 °C, 50 % relative humidity, and a weight hourly space velocity (WHSV) of 560,000 mL g-1h−1. Even under harsh conditions of 90 % relative humidity, the conversion efficiency remained at 70 % after 8 h. We investigated the effects of acid treatment on the catalysts and found that potassium ion decrease resulted in the formation of nanoflower-like structures and enhanced the mobility of oxygen species, accelerating ozone decomposition. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations indicated that the potassium ion decrease contributed to the formation of oxygen vacancies and enhanced the water resistance of the catalysts. Moreover, we revealed the decomposition mechanism of ozone when coexisting with water molecules, which provided new insights for related studies.
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:160769
卷号:671
是否译文:否
发表时间:2024-09-29
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016943322401482X?pes=vor
上一条: Mechanistic effects of surface functional groups on porous carbons for hydrogen purification: Multi-scale simulation perspective of competitive adsorption behavior
下一条: Mechanistic effects of graphitization and oxygen functional groups on benzene competitive adsorption of porous carbon under high humidity conditions