Mechanistic effects of surface functional groups on porous carbons for hydrogen purification: Multi-scale simulation perspective of competitive adsorption behavior
发布时间:2025-04-10
点击次数:
DOI码:10.1016/j.cej.2024.158989
所属单位:中南大学
发表刊物:Chemical Engineering Journal
关键字:Adsorption behavior; DFT; GCMC; Hydrogen purification; Porous carbons; Surface functional groups
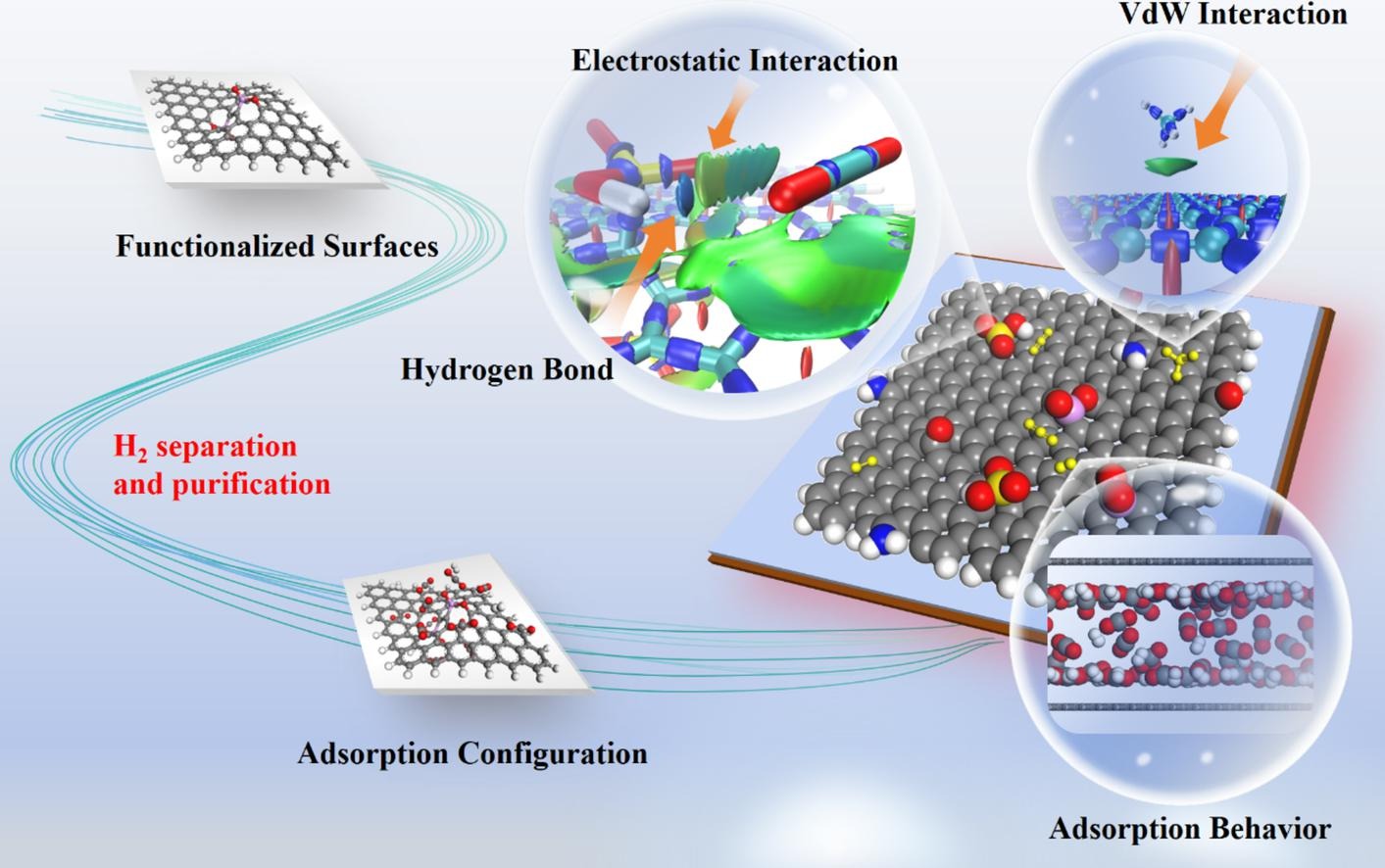
摘要:Efficiently and selectively purifying hydrogen from multi-component gas mixtures has emerged as a pivotal aspect in the hydrogen economy. Herein, the separation properties and mechanistic effects of porous carbons for rich hydrogen mixtures were investigated. It focused on the competitive adsorption behavior of H2 over N2, CO2 and CH4 in surface-functionalized graphene models (G-Rs, R = –C[dbnd]O, –NH2, –SO3H, –(CO)C2–PO), and explored its separation mechanism at a microscopic level. The results showed that for surface functional groups, G-Rs exhibit a superior H2 separation performance than G-None (pristine graphene model) due to the stronger electrostatics interaction. Specially, G-(CO)C2–PO exhibited the highest N2/H2, CO2/H2 and CH4/H2 adsorption selectivity of 7.3, 1179.4 and 53.4, respectively, which was an enhancement of 73 %, 615 % and 383 % than that of G-None. In addition, the competitive adsorption effect was analyzed through two hypothetical paths for the adsorption process of CO2/H2 gas mixture on porous carbons. To be specific, the H2 and CO2 molecules would occupy the different active adsorption sites due to the various weak interactions between gas molecules and adsorption surfaces, resulting in the different adsorption behaviors. Furthermore, the intrinsic mechanism of H2 separation property on porous carbon was also evaluated by scanning the potential energy surface and analyzing the charge density difference. This work provides a novel insight into the strategy of designing promising porous carbons for effective H2 purification and recovery.
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:158989
卷号:504
是否译文:否
发表时间:2025-01-15
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894724104809?via%3Dihub