Research FieldsBased on remote sensing and geographic information technologies, we attempt to overcome the limitation of sparse ground-level monitoring sites and hypothesis for popular advanced statistical modeling, and carry out air pollution mapping, exposure risk assessment, and spatial information service research.
1. Geographic Information Science and Technology Progress Award of China (Extra Prize),2017 2. Science and Technology Progress Award for Surveying and Mapping of China (Second Prize),2017 3. Zou, B, Zhan, F. B, Zeng Y., Space-time modeling and risk assessment of air pollution exposure (Book) , 2012.12. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. ISBN: 978-7-5111-1106-7. 4. Zou, B*., Wilson, J. G., Zhan, F. B., et al.2009. Air pollution exposure assessment methods utilized in epidemiological studies. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11(3): 475-490. 5. Zou, B*., Wilson, J. G., Zhan, F. B., et al.2009. Spatially differentiated and source-specific population exposure to ambient urban air pollution. Atmospheric Environment, 43(26), 4005-4013. 6. Zou, B*., Wilson, J. G., Zhan, F. B., et al.2009. An emission-weighted proximity model for air pollution exposure assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 407(17), 4939-45. 7. Zou, B*., Luo Y, Wan N, et al. Performance comparison of LUR and OK in PM2.5 concentration mapping: a multidimensional perspective. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(5):8698. 8. Fang, X., Zou, B*., Liu, X., et al. 2016. Satellite-based ground PM2.5 estimation using timely structure adaptive modeling. Remote Sensing of Environment, 186, 152-163. 9. Zou, B*., Pu, Q., Bilal, M., et al. 2016. High-resolution satellite mapping of fine particulates based on geographically weighted regression. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 13(4), 495-499. 10. Zou,B*., Chen, J., Zhai, L., et al. 2016. Satellite based mapping of ground PM2.5 concentration using generalized additive modeling. Remote Sensing,9(1),1.
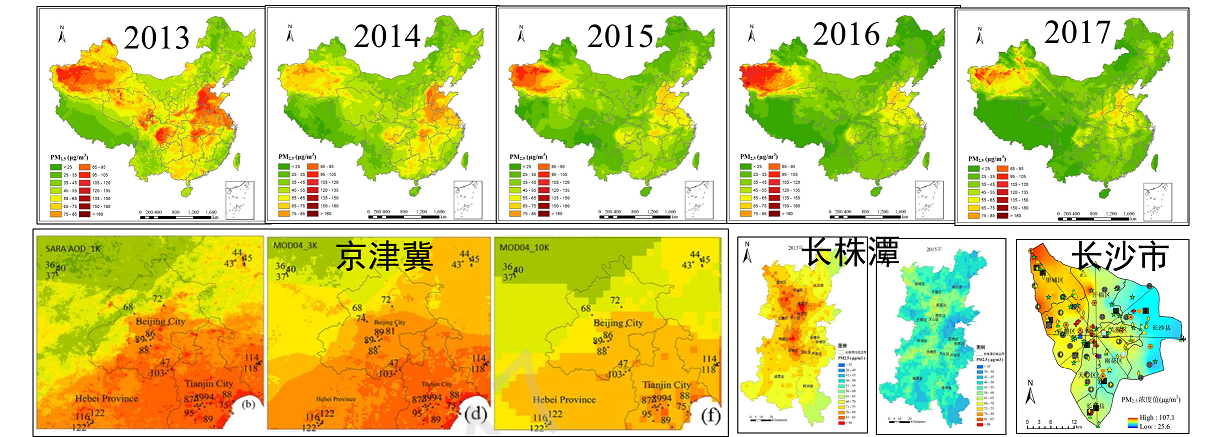
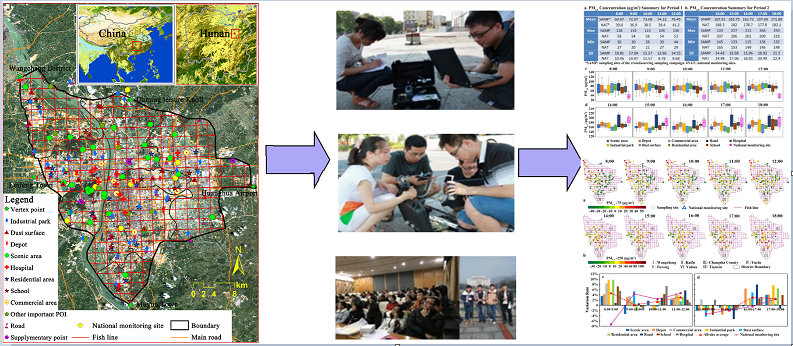
Mapping of PM2.5 concentration at different temporal and spatial scales Crowdsourcing sampling campaign and data modeling analysis of air quality concentrations
(2) Fine Measurement of Spatial-temporal Air Pollution Exposure and Big Data Waring Platform. We focus on providing real-time air pollution information and effective warning services which taking human oriented fine measurement of air pollution exposure for different populations and individuals based on spatio-temporal big data. The achievements are as follows.
1. Zou B*, Zheng Z, Wan N, et al. 2015. An optimized spatial proximity model for fine particulate matter air pollution exposure assessment in areas of sparse monitoring. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 30(4):727-747 2. Zou Bin, Zhan F.B., 2016. Air Pollution Exposure Assessment and Environmental Health Risk Analysis (Chapter 6), Application of Geographic Information Science in Public Health and Health, Beijing: Higher Education Press. ISBN: 978 -7-04-044052-2. 3. Shi Xun, Wang Fahui, Zou Bin, et al., 2016. Application of Geospatial Analysis in Public Health Research in China: Progress and Prospects (Chapter 13), Application of Geographic Information Science in Public Health and Health, Beijing: Higher Education Press. ISBN: 978-7-04-044052-2. 4. Ministry of Environmental Protection, 2016. China Population Exposure Parameter Manual (Children, Volume 0-5) (Hardcover) & Chinese Population Exposure Parameter Manual (Children's Volume 6-17) (Hardcover) & Chinese Population Environment Exposure Behavior Model Study Report (Children's Volume), writing group members. 5. A road route selection method based on low air exposure risk, national invention patent (ZL20141047513.5, authorized) 6. A public air pollution exposure risk measurement index calculation method, national invention patent (201810207295.8, accepted) 7. Air Pollution Data Collection and Management System V1.0, Computer Software Copyright (2017SR378310) 8. Exposure risk visualization monitoring platform, computer software copyright (2018SR218303) 9. Individual PM2.5 exposure simulation measurement APP software V1.0, computer software copyright (2018SR218291) 10. Healthy Travel Path Planning App Software, Computer Software Copyright (2018SR279436)
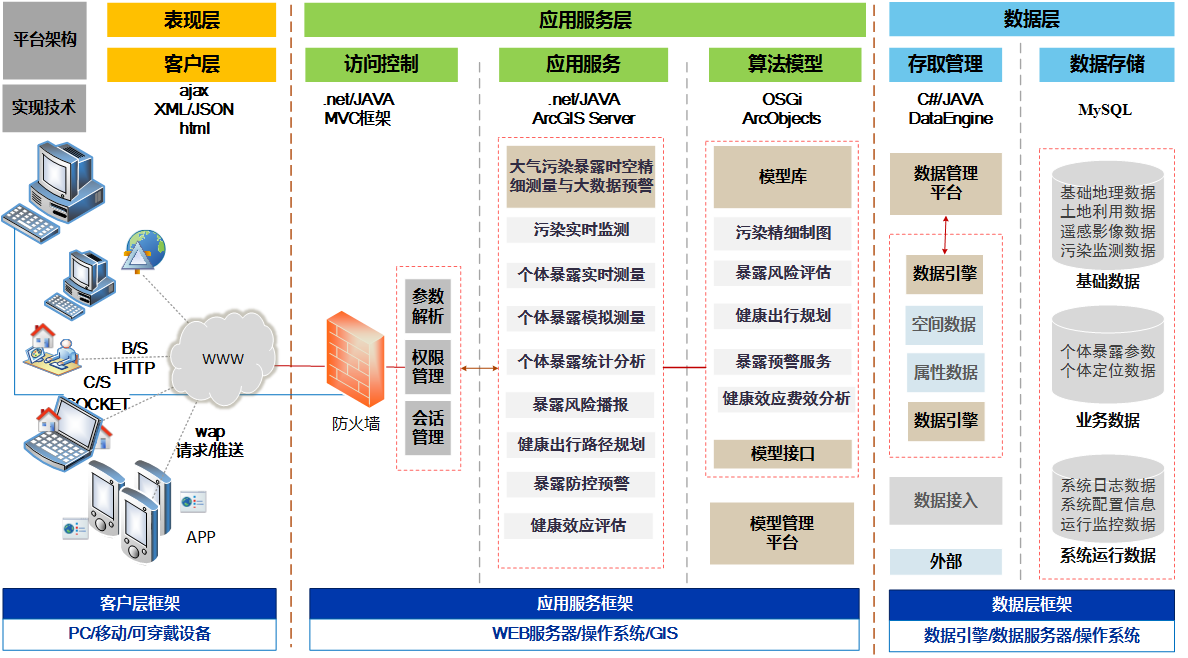
Framework of a fine measurement of spatio-temporal air pollution exposure aplatform
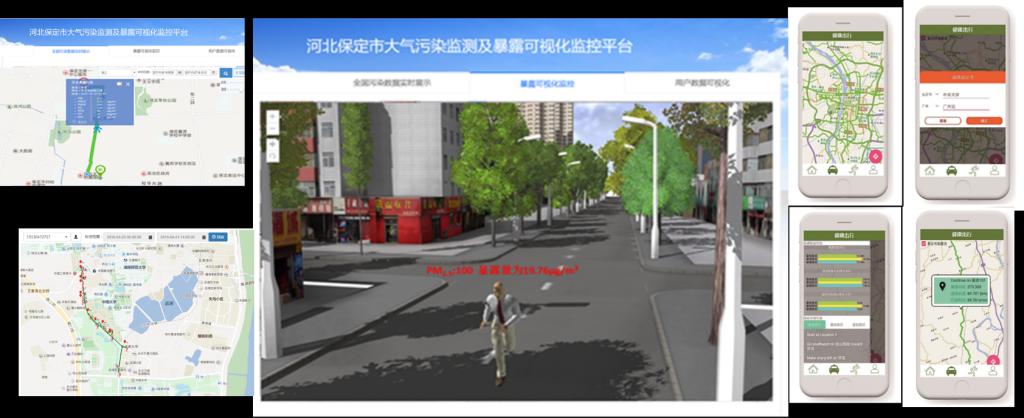
A system and APP for fine measurement of individual spatio-temporal air pollution exposure
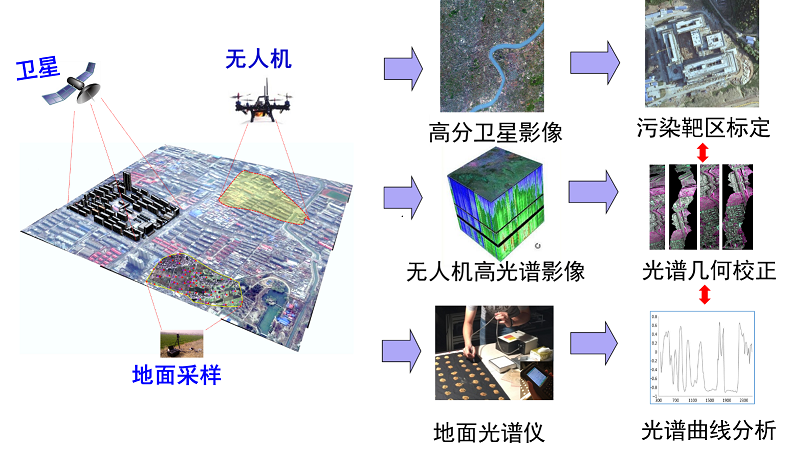
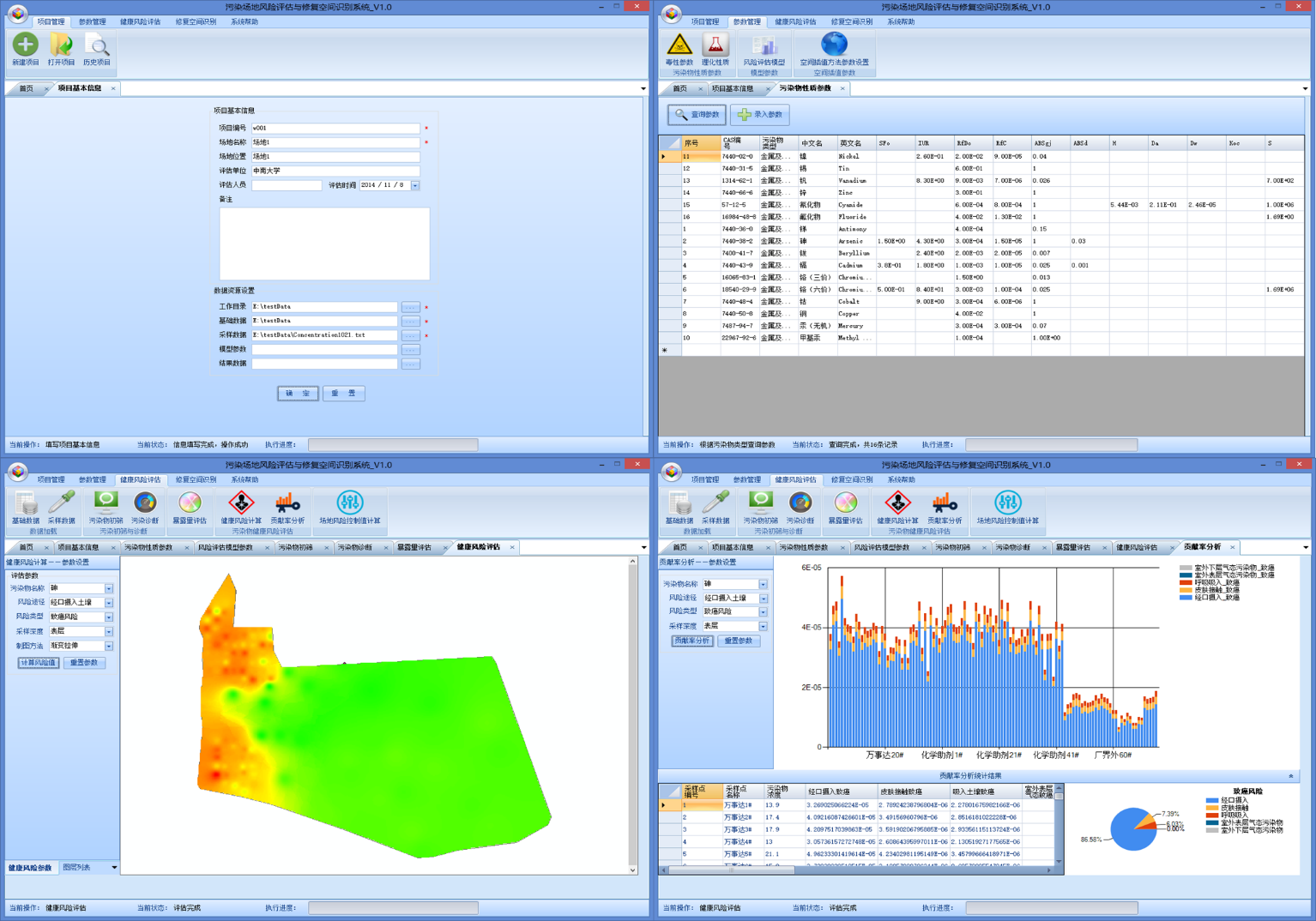
1. Ministry of Education Reward: As a member of the National Yellow University Teacher Team, 2017. 2. Hunan Science and Technology Innovation Award: R&D and application of heavy metal pollution prevention and control technology in Xiangjiang River Basin, 2017. 3. Zou, B*., Jiang, X., Duan, X., et al. 2017. An integrated H-G scheme identifying areas for soil remediation and primary heavy metal contributors: a risk perspective. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 341. 4. Sun, W., Zhang, X*., Zou, B., et al. 2017. Exploring the potential of spectral classification in estimation of soil contaminant elements. Remote Sensing, 9(6), 632.2. 5. Tu, Y., Zou, B*, Jiang, X., et al. 2018. Hyperspectral remote sensing based modeling of Cu content in mining soil. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 38(2): 575-581. 6. Tao, C., Wang, Y., Zou, B*., et al. 2018. Evaluation and analysis of migratory capacity of hyperspectral inversion model for heavy metal lead and zinc. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 38(6): 1-6. 7.Jiang X., Zou B*, et al. 2016. Spatial distribution of arsenic content in vegetable fields in southeastern Guangdong Province (in Chinese). Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 32(23): 263-268. 8. Inversion modeling of soil heavy metal Cd content based on indoor standard hyperspectral characteristics and spectral response characteristic band identification method, national invention patent (201710120751.0, substantive examination stage). 9. A method for inversion of heavy metal content in combined indoor and outdoor spectra, national invention patent (201810233070.X, accepted). 10. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Risk Assessment System, Computer Software Copyright (2012SR108000). Space-Air-Ground integrated detection based on hyperspectral remote sensing The fine spatial identification system for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation
1. Dong Minghui, Zou Bin, Peng Baofa. 2014. “Research on Dongting Lake-Resource Utilization, Environmental Protection and Regional Development”. Changsha: Central South University Press. ISBN: 978-7-5487-1059-2. 2. Zou, B*., Xu, S., Sternberg, T., et al. 2016. Effect of land use and cover change on air quality in urban sprawl. Sustainability, 8(7), 677. 3. Wong, M. S., Peng, F., Zou, B*., et al. 2016. Spatially Analyzing the Inequity of the Hong Kong Urban Heat Island by Socio-Demographic Characteristics. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health, 13(3):317. 4. Feng, H., Zou, B*., Tang Y. 2017. Scale- and Region-Dependence in Landscape-PM2.5 Correlation: Implications for Urban Planning. Remote Sensing, 9(9):918. 5. Feng, H., Zou, B*., Luo J. 2017. Coverage-dependent amplifiers of vegetation change on global water cycle dynamics. Journal of Hydrology, 550. 6. Feng, H., Liu, H., Lv, Y., 2012. Scenario Prediction and Analysis of Urban Growth Using SLEUTH Model. Pedosphere, 22(2): 206-216. 7. Tang, Y., Zhang, L, 2017. Urban Change Analysis with Multi-Sensor Multispectracl Imagery. Remote Sensing, 9(3), 252. 8. Tang, Y., Lan, Y., Feng, H. 2018. Effect Analysis of Land-use Pattern with Landscape Metrics on An Urban Heat Island. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 12(2): 026004 . Remote Sensing Monitoring of Land Use Change in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan city cluster Evolution of urban heat islands and the contribution from land use change in Xiamen |
|