1.BACTERIAL COMMUNITY SUCCESSION AND POSTMORTEM INTERVAL(PMI)
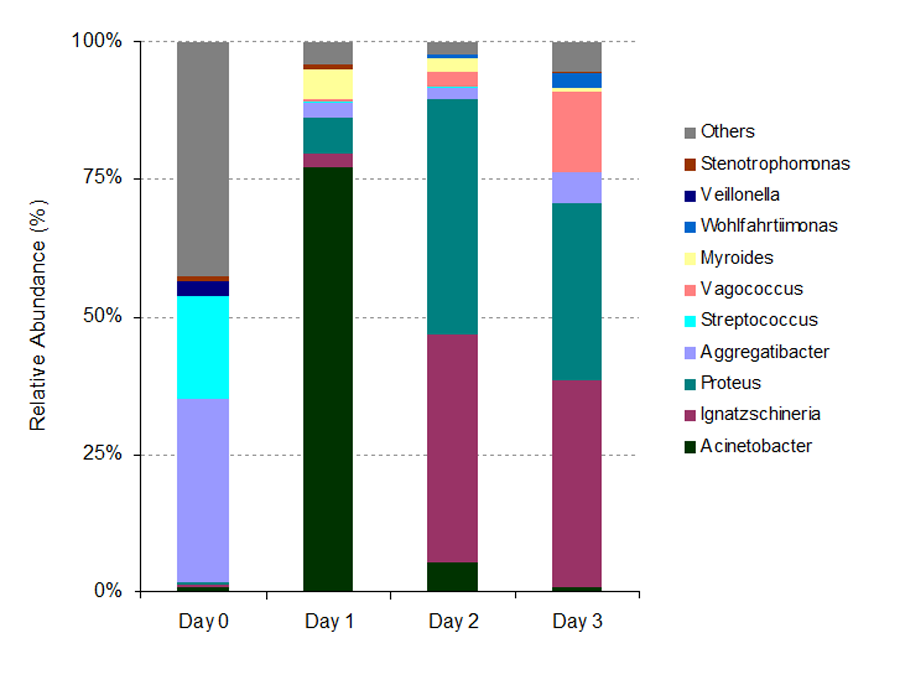
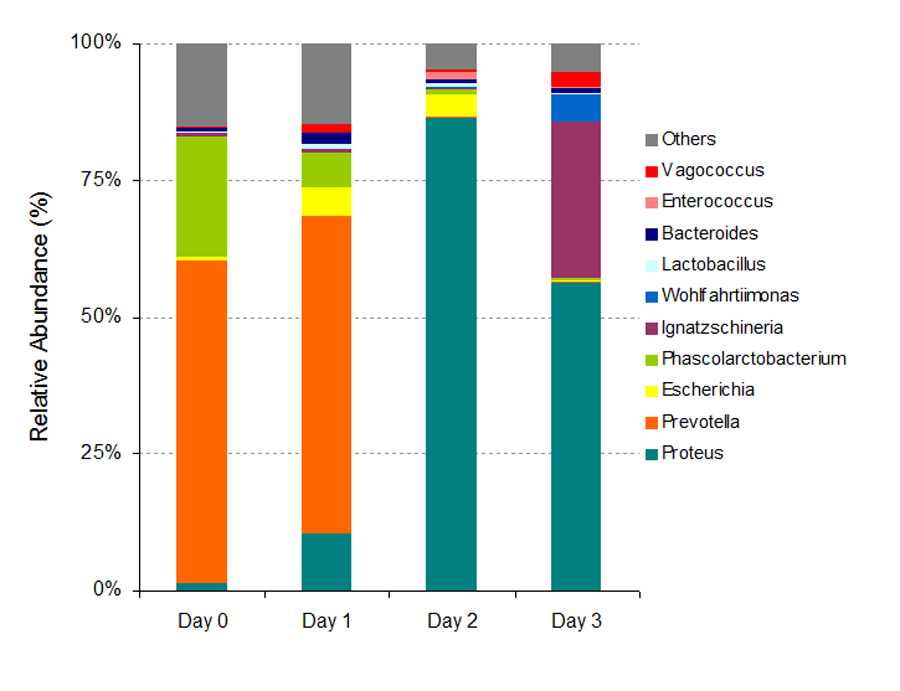
The estimation of postmortem interval (PMI) is one of the most difficult tasks in forensic practice, especially in putrefied bodies. After death, organisms are decomposed by a variety of enzymes and microorganisms. To investigate the succession of bacterial community in the decomposition process, rat remains were placed outside to decompose under natural conditions in Changsha city, China. Bacterial communities from two regions (buccal cavity and rectum) were sampled when experiment animals were alive, soon after they died and at various time span after death. Bacterial samples were analyzed by high throughput metagenomic sequencing of 16S rRNA gene conducted on an Illumina MiSeq platform. Our data showed that several bacteria genera were potentially useful for estimating the PMI, such as Streptococcus, Ignatzschineria, Acinetobacter, Aggregatibacter, Prevotella and Proteus. There were significant bacterial community structure differences in taxon richness and relative abundance patterns through the decomposition process and across different body sites. As decomposition progressed, a negative linear relationship for taxon richness was found along with a shift from aerobic bacteria to anaerobic bacteria. We first reported the bacterial biodiversity in the decomposition process in Chinese terrestrial scenarios and climatic conditions. Bacteria have a remarkable potential for estimate the PMI and next generation sequencing is a novel method to support the application of bacteria in forensic science.
|
|
Figure 1 Bacterial community structure in buccal cavity at the genus level. Only the top ten genera are listed. |
Figure 2 Bacterial community structure in rectum at the genus level. Only the top ten genera are listed. |
2.THE POTENTIAL USE OF FUNGI COMMUNITY IN POSTMORTEM INTERVAL ESTIMATION IN CHINA
Estimation of postmortem interval (PMI) with fair accuracy is a critical step in death investigations. Although many approaches are available to estimate PMI through physical findings and biochemical tests, accurate PMI calculation by these conventional methods is still difficult because it is readily affected by surrounding conditions, such as ambient temperature and humidity. It is reported that body provides a residence for diverse commensal microbiota. Microorganisms such as fungi have major roles in this microbial community stability and post- putrefaction fungi have been recorded several times in association with decomposed mammalian cadavers in disparate regions. The succession and diversity of these fungi are reviewed with a view to their potential as a forensic tool. The research of mycology is an interface to forensic investigation and may provide a means to estimate PMI within serious decomposition. To evaluate the use of succession and diversity of fungi species for PMI estimation, we investigated the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) of fungi community on 3 points of time of rat carcasses conducted by Illumina MiSeq platform. Through high-throughput sequencing, several fungi genus such as Mrakia and Amorphotheca are found in community succession (Fig. 1) and the community structure of each sample significantly differs in overall taxon richness and relative abundance patterns within decomposition progress (Fig. 2). The succession and diversity of fungi community in corpse decomposition revealed by the indicator of ITS would be a potential forensic tool for PMI estimation.
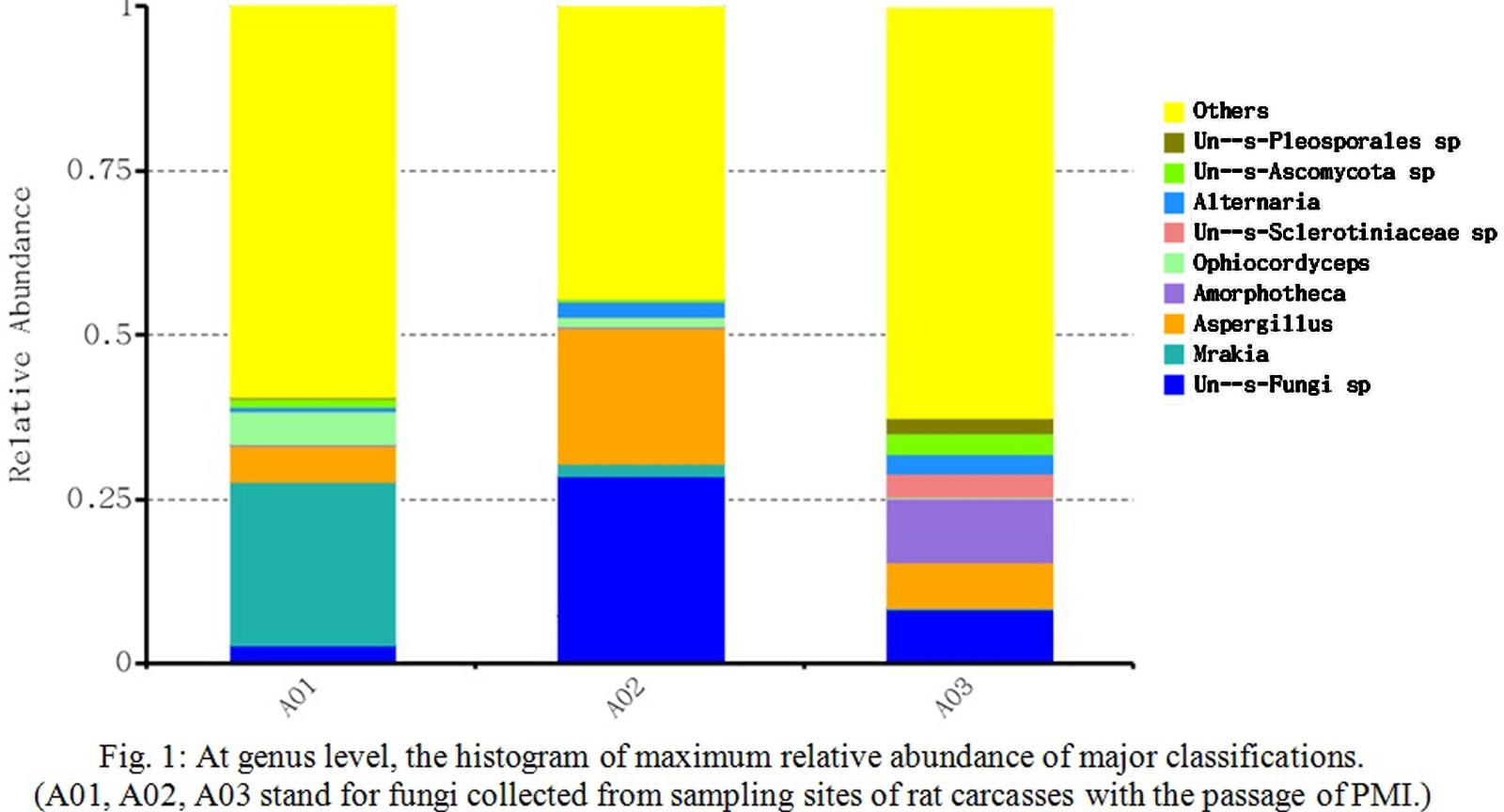
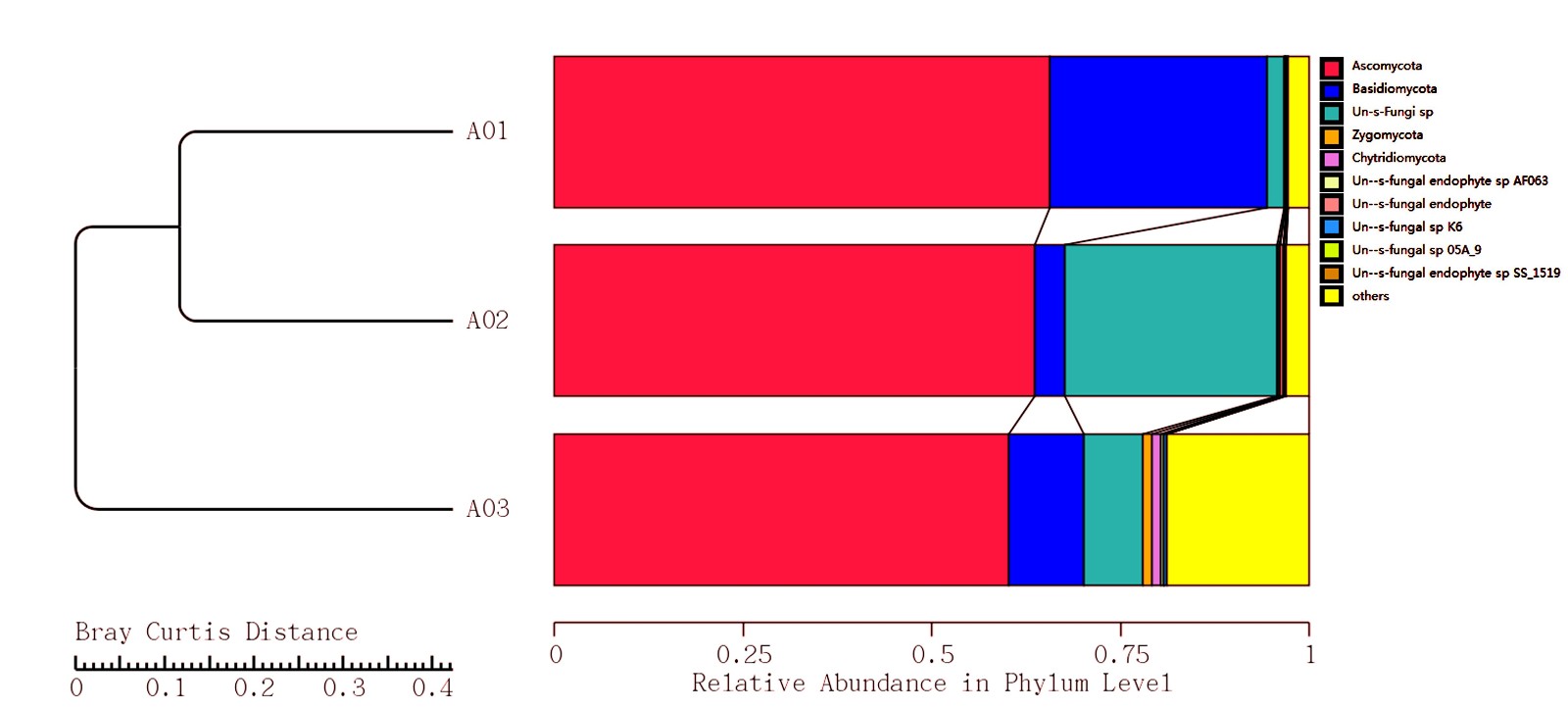
Fig. 2: At phylum level, the histogram of maximum relative abundance of 10 top classifications
and the Bray Curtis distance between each samples.
(A01, A02, A03 stand for fungi collected from sampling sites of rat carcasses with the passage of PMI.)