李广超博士论文“Metalorganic Quantum Dots and Their Graphene-Like Derivative Porous Graphitic Carbon for Advanced Lithium Ion Hybrid Supercapacitor”被Advanced Energy Materials接收发表
发布时间:2020-04-25
点击次数:
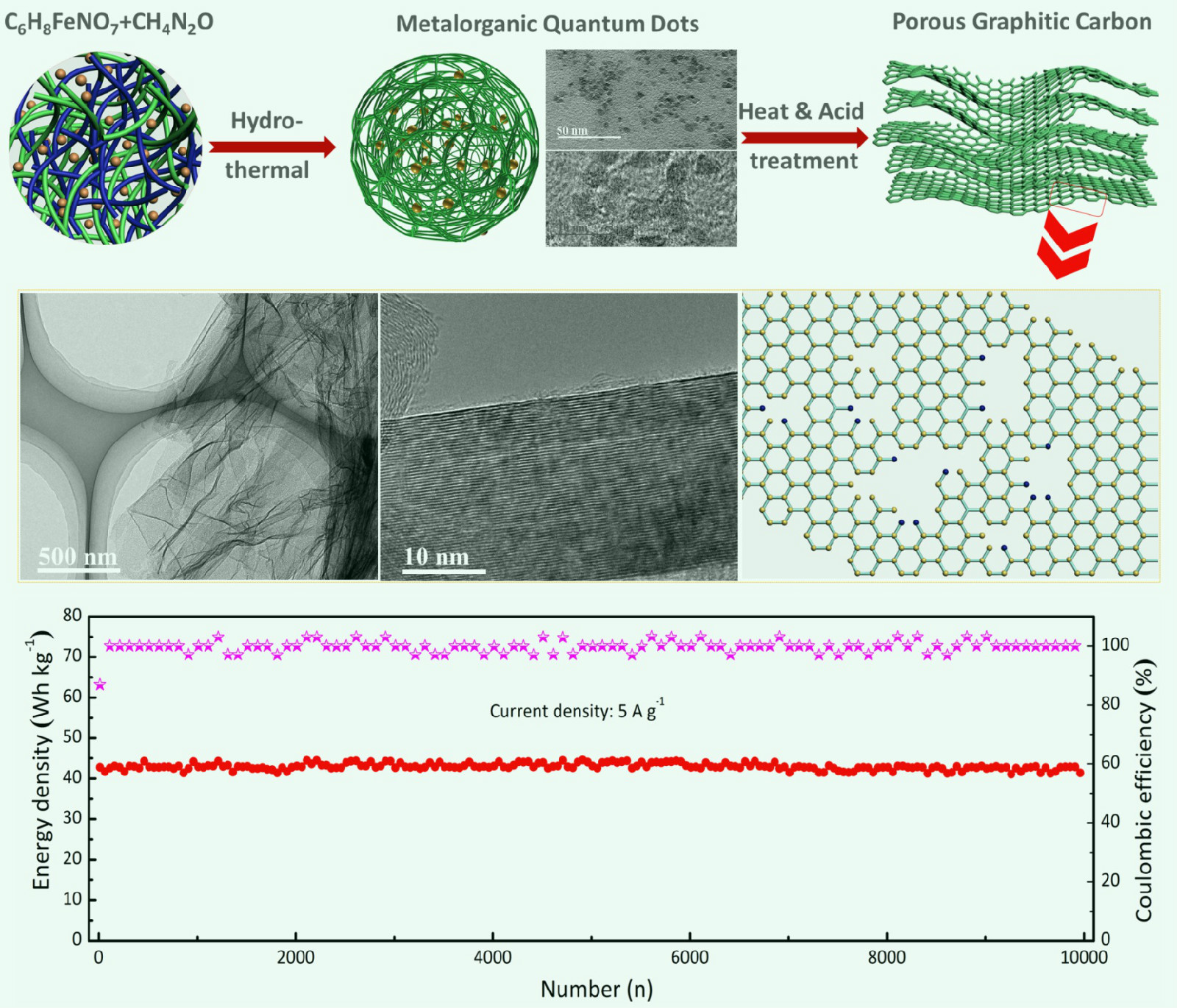
Lithium-ion hybrid supercapacitors are considered as a promising candidate in energy storage systems. Especially the battery-type anode plays a significant role in high-power-density and long-term-cycle-life lithium-ion hybrid supercapacitors taking the factor of its sluggish kinetics behavior compared to the capacitive cathode into consideration. Here, onion-shaped graphene-like derivatives are synthesized via carbonization of metalorganic quantum dots (MQDs) accompanied with in-situ catalytic graphitization by reduced metal. Notably MQDs, exhibiting water-soluble character and ultrafine particles (2.5-5.5 nm) morphology with uniform element distribution, are prepared by the amidation reaction. The carbonized sample exhibits highly graphitic tendency with graphitization degree up to 95.6%, and shows graphene-like porous structure, appropriate amorphous carbon decoration characteristic, as well as N doping and defective nature. When employed as anode materials for LICs, both high reversible specific energy and superior rate property are achieved. In particular, it shows high energy density of 83.7 Wh kg-1 and high power density of 6527 W kg-1 when the mass ratio of cathode to anode is calculated as 1:1 and the operating voltage ranges from 2.0–4.0 V. It also possesses the long cyclic stability with the energy density retention maintains at 97.3% after 10,000 cycles at 5.0 A g-1. The energy density reaches to 114.3 Wh kg-1 and 153.0 Wh kg-1 respectively at 0.05 A g-1 when the mass ratio of cathode to anode enlarges to 4:1 or working voltage extends to 1.5–4.5 V. This work provides us a novel strategy to develop high-performance porous graphitic carbon materials for new-type energy storage.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/aenm.201802878